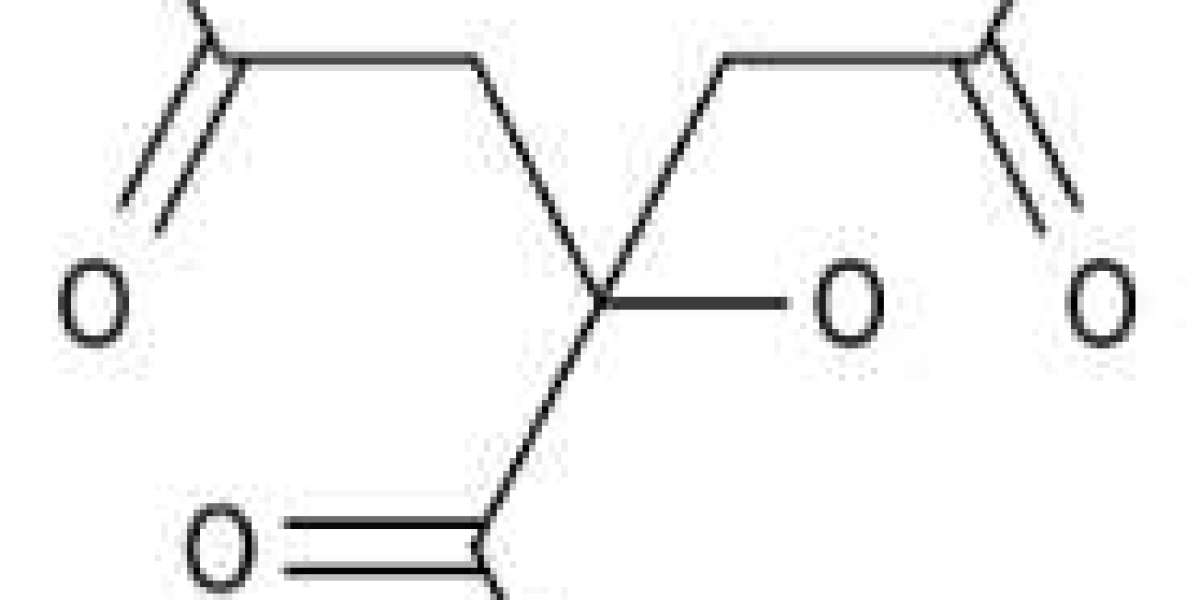
Citric acid is a weak organic tricarboxylic acid found in citrus fruits. Citric acid is a natural preservative and food tartness enhancer.
Use and Manufacturing
1. Citric acid is a weak organic acid that is known as a commodity chemical, as more than a million tonnes are produced every year by mycological fermentation on an industrial scale using crude sugar solutions, such as molasses and strains of Aspergillus niger. Citric acid is widely distributed in plants and animal tissues and fluids and exists in greater than large amounts in a variety of fruits and vegetables, most notably in citrus fruits such as lemon and limes. Citric acid is mainly used as an acidifier, flavoring agent, and chelating agent.
2. Used in sequestering agents for trace metals; determination of citrate-soluble phosphorus pentoxide.
Citric acid (CA), also known as citric acid, with the molecular formula C ₆ H ₈ O ₇, is an important organic acid. It is a colorless crystal, odorless, has a strong acidic taste, and is easily soluble in water. It is an acidity regulator (GB2760-2014) and a food additive.
Physical and chemical properties
Structurally speaking, citric acid is a type of tricarboxylic acid compound and therefore has similar physical and chemical properties to other carboxylic acids. Citric acid is a strong organic acid with 3 H+ions that can ionize.
At room temperature, citric acid is a white crystalline powder, odorless and extremely sour, with a density of 1.542g/cm3, a melting point of 153-159 ℃, and decomposes above 175 ℃ to release water and carbon dioxide. Citric acid is easily soluble in water, with a solubility of 59g at 20 ℃, and a pH of 2.1 for its 2% aqueous solution. The crystalline form of citric acid varies depending on the crystallization conditions, with slight weathering in dry air and hygroscopicity in humid air. Heating can decompose into various products and react with acids, bases, glycerol, etc. When citric acid is dissolved in ethanol, it reacts with ethanol to produce ethyl citrate.
Ionization situation
The ionization constant of citric acid is pK1=3.13; PK2=4.76; PK3=6.40, from the ionization constant, citric acid is relatively strong. The main form of citric acid after ionization is related to pH. Under the pH conditions of electroless nickel plating, the vast majority of citric acid has been ionized into trivalent citrate ions.
Search
Popular Posts
-
 What Makes WOL3D Coimbatore Your Best Choice for 3D Printer Filament Online?
What Makes WOL3D Coimbatore Your Best Choice for 3D Printer Filament Online?
-
 Explore Creativity with WOL3D Coimbatore's Best 3D Printers in Kerala
Explore Creativity with WOL3D Coimbatore's Best 3D Printers in Kerala
-
 Implement at least 2 hours of sports activities every day
By jessicp
Implement at least 2 hours of sports activities every day
By jessicp -
 The national operator is obliged to formulate the terms
By jessicp
The national operator is obliged to formulate the terms
By jessicp -
College Essay Conclusion: Tips for Writing One!
By cloudebaker