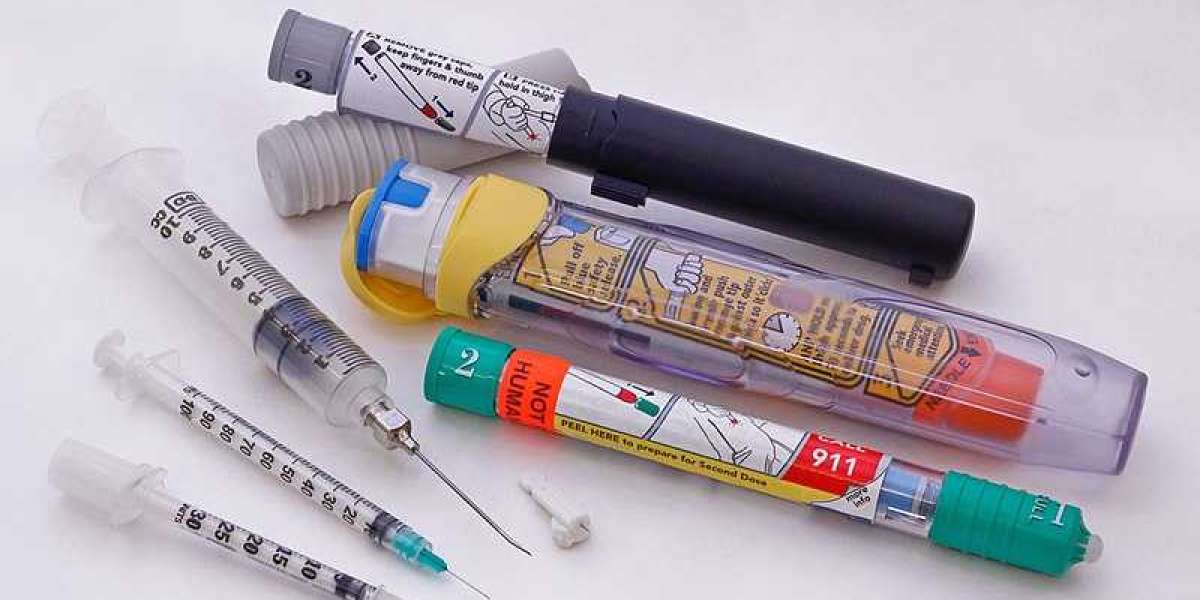
Biohazard waste, also known as biomedical waste, is a type of hazardous waste that poses a potential threat to human health or the environment due to its infectious nature. Proper disposal of biohazard waste is essential to prevent the spread of diseases and protect public safety. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the regulations governing biohazard waste disposal.
Understanding Biohazard Waste:
Biohazard waste includes materials contaminated with blood, bodily fluids, pathogens, and other infectious agents. It is generated in various settings, such as healthcare facilities, laboratories, and research institutions, as well as in industries involving biological materials.
Regulatory Agencies:
Biohazard waste disposal is subject to regulations established by different agencies, including:
a. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): EPA regulations focus on the management of hazardous waste, including some biohazard materials.
b. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for the safe handling of biohazard waste and the protection of workers.
c. State and Local Agencies: States and local jurisdictions often have their own regulations that may be more stringent than federal requirements.
Biohazard Waste Categories:
Biohazard waste is typically categorized into several groups, such as:
a. Infectious Waste: Materials that contain pathogens capable of causing diseases in humans.
b. Pathological Waste: Includes human tissues, organs, and body parts.
c. Sharps Waste: Objects that can cause puncture or laceration injuries, such as needles, syringes, and scalpels.
d. Chemical Biohazard Waste: Waste materials contaminated with chemicals used in laboratories, research, or medical procedures.
Packaging and Labeling:
Proper packaging and labeling are crucial for the safe handling and disposal of biohazard waste. Regulations often require the use of leak-proof, puncture-resistant containers labeled with biohazard symbols and other identifying information.
Storage Requirements:
Biohazard waste must be stored in designated areas that meet specific requirements, including secure containers and controlled access to prevent unauthorized personnel from handling the waste.
Transportation Regulations:
Transporting biohazard waste from the generation site to treatment or disposal facilities must comply with strict regulations. Properly labeled, sealed containers are used, and transportation vehicles are equipped to prevent spills or accidents during transit.
Treatment and Disposal:
Biohazard waste must undergo appropriate treatment methods to inactivate or sterilize pathogens before disposal. These methods may include incineration, autoclaving, or chemical treatment. The choice of method depends on the type of waste and regulations.
Record-Keeping and Reporting:
Regulatory compliance often requires meticulous record-keeping and regular reporting of biohazard waste management activities. This documentation ensures transparency and accountability in the waste disposal process.
Worker Safety:
Regulations, especially those set by OSHA, focus on protecting the safety and health of workers who handle biohazard waste. This includes training on proper handling, the use of personal protective equipment, and vaccinations for specific diseases.
Penalties for Non-Compliance:
Failure to comply with biohazard waste regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines and legal consequences. Non-compliance also poses risks to public health and the environment.
Conclusion:
Biohazard waste disposal regulations are vital for protecting public health and the environment from infectious and hazardous materials. Businesses and institutions generating biohazard waste must adhere to these regulations to ensure safe and responsible waste management. Staying informed about federal, state, and local requirements and implementing best practices for handling, transporting, and disposing of biohazard waste is essential for compliance and public safety.