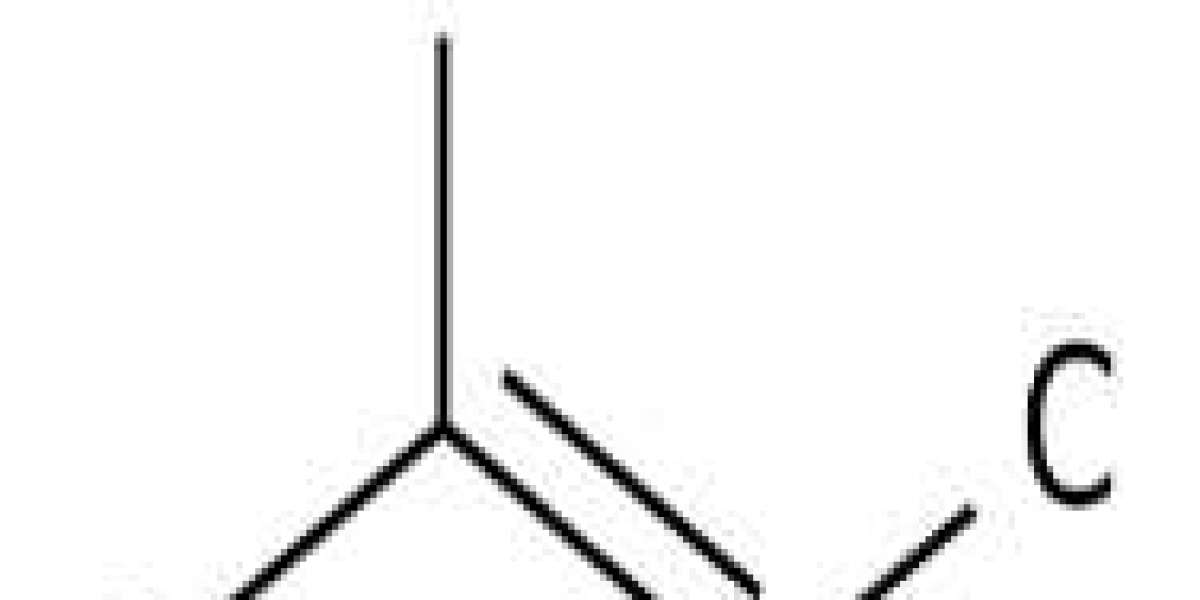
2-Methyl-2-butanol (tert-amyl alcohol, t-AmylOH, MBY) has been used as solvent for the dissolution of avertin [2,2,2-tribromoethanol), which was employed as an anesthetic in immunohistochemical study. It has been used in the preparation of (E)-2-(2-(3-ethoxy-3-oxoprop-1-enyl)-6-fluorophenyl)acetic acid.
2-Methyl-2-butanol is an isomeric form of pentanol. Various physical properties (static dielectric constant, viscosity, density, ultrasonic and dielectric relaxation) of 2-methyl-2-butanol have been evaluated over a wide range of temperatures. Its ability as solvent in the extraction of furfural from aqueous solutions has been tested. Kinetic parameters of the three-phase reaction of MBY with hydrogen catalyzed by a commercial palladium-based catalyst in the absence of solvent have been described.
2-Methyl-2-butanol, also known as t-amyl alcohol or 2m2b, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tertiary alcohols. Tertiary alcohols are compounds in which a hydroxy group, -OH, is attached to a saturated carbon atom R3COH (R not H ). 2-Methyl-2-butanol is a pungent tasting compound. 2-Methyl-2-butanol is found, on average, in the highest concentration within grape wine. 2-Methyl-2-butanol has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as evergreen blackberries (Rubus laciniatus), orange bell peppers (Capsicum annuum), blackberries (Rubus), green bell peppers (Capsicum annuum), and celeriacs (Apium graveolens var. rapaceum). This could make 2-methyl-2-butanol a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Based on a literature review a significant number of articles have been published on 2-Methyl-2-butanol.
2-Methyl-2-butanol is an organic compound that has the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2OH. It is a colorless liquid that is moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most organic solvents. 2-Methyl-2-butanol is a reactive compound and can be classified as an alcohol. This alcohol reacts with hydroxyl groups to form ethers and esters, which are important intermediates in many chemical reactions. 2-Methyl-2-butanol also has been shown to inhibit the HIV virus by binding to its reverse transcriptase protein and preventing it from synthesizing DNA. Kinetic data for this reaction have been collected using p-nitrophenyl phosphate as a substrate. The enzyme inhibitors hydrogen bond and picolinic acid have been shown to react with 2-methyl-2-butanol, resulting in the formation of fatty acid esters. Humans metabolize 2-methyl-2 butanol primarily by oxidation of
2-methylbutan-1-ol is a primary alcohol that is isopentane substituted by a hydroxy group at position 1. It has a role as a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite. It is an alkyl alcohol and a primary alcohol. It derives from a hydride of an isopentane.
2-Methyl-1-butanol is a natural product found in Aloe africana, Myrtus communis, and other organisms with data available.
Search
Popular Posts
-
 What Makes WOL3D Coimbatore Your Best Choice for 3D Printer Filament Online?
What Makes WOL3D Coimbatore Your Best Choice for 3D Printer Filament Online?
-
 Explore Creativity with WOL3D Coimbatore's Best 3D Printers in Kerala
Explore Creativity with WOL3D Coimbatore's Best 3D Printers in Kerala
-
 Implement at least 2 hours of sports activities every day
By jessicp
Implement at least 2 hours of sports activities every day
By jessicp -
 The national operator is obliged to formulate the terms
By jessicp
The national operator is obliged to formulate the terms
By jessicp -
College Essay Conclusion: Tips for Writing One!
By cloudebaker